Almost everyday I work with individuals who are victims of attempted internet scams. More often than not the attempt can be thwarted by immediate action and remediation. In some cases, the scam is successful and profits the Cyber criminal.
In this article series I will describe a few of the scams witnessed. From fake Microsoft pop-ups, faux Apple support numbers, and phishing attempts, I hope this series proves to help those who are targeted.
Microsoft Pop-Ups
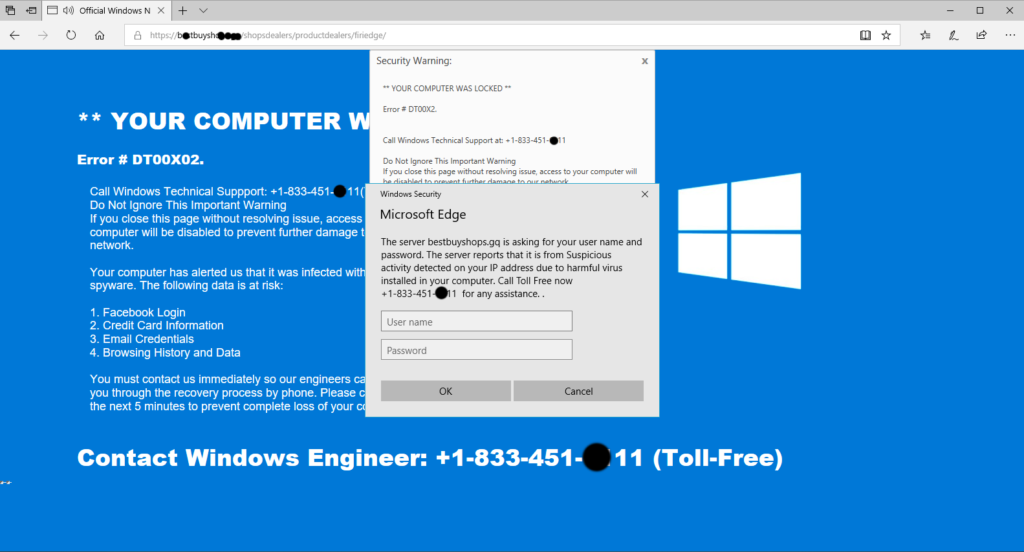
What are they?
These are pop-ups that claim to be Microsoft support, often supplying a phone number for you to call. They often include loud noises and alarms to induce panic in the user. In some situations it will also prevent you from closing the pop-up by preventing you from clicking the ‘X’.
Why?
The goal for the scammers is for you to call the phone number provided. When you call they will usually instruct you on how to grant them access to your computer to fix the issue. This usually entails a fee of around $300. After bringing some prompts on your screen and developing a very intriguing story on how hackers are infiltrating your computer, you may be inclined to pay up.
What do I do?
First, do not panic and do not give your card information to anyone. If you have given them credit card or banking information, call the respective bank and report that your account has been compromised, reporting any fraudulent charges immediately.
If you are on the phone with them, hang up and turn off the computer (if they are actively controlling it and you have given them access).
Stuck at the pop-up?
Attempt to use the hotkey to close the current window, you can do this by holding the ‘Alt’ key and pressing ‘F4’. This should close the current pop-up window and allow us to continue. If not, attempt to open task manager using ‘Ctrl’+’Shift’+’Esc’ and close the applications/processes associated with your web browser (Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Chrome). If all else fails, shutdown/restart the computer.
Next, we need to clean up some things in our web browser. The pop-up is probably still residing in our history, or recently opened tabs. We want to minimize the risk of receiving that pop-up again.
Follow one of the following guides; Reset Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, or Google Chrome
NOTE: Resetting your browser will remove extensions and add-ons but will not remove bookmarks or passwords.
Now we want to remediate any damage done, or remove any malicious files on our system. My recommendation is to use some free software supplied by Malwarebytes. Run a scan with the following and feel free to remove them afterwards if you choose.
Download, install, and scan with both Malwarebytes Anti-Malware and AdwCleaner from this page; malwarebytes.com
NOTE: Malwarebytes Anti-Malware will start with a free 14-day trial of their premium subscription, but may be changed to their completely free version.
Summary
Luckily in most cases, these scammers are not very skilled, they follow a script in hopes of easy money. Any damage done can usually be reversed. Take some time to practice safe internet use with this article from getsafeonline.org
As always, stay safe and be on the lookout for future articles from IT Wes. Thank you!
Coming soon..
Common Online Scams and Cyber Crime: Fake Support Phone Numbers
Common Online Scams and Cyber Crime: Phishing Attempts via Phone Calls & Emails